Mattress Testing Policy
Updated: January 15, 2026 | Published: August 21, 2025Third-party engineers (who we commissioned) assess each mattress’s performance in a controlled setting. Our latest stamped engineering report is publicly accessible and can be viewed anytime. Mattress test scores are calculated and weighted against mattresses in the same category (i.e., foam or hybrid) on a scale of 1–10.
Weightings vary by category because these mattress types are constructed differently. A foam mattress scoring 7.5/10 for edge support isn’t the same as a hybrid mattress scoring 7.5/10. It’s best to compare similar mattress types while you’re shopping to get the most accurate comparison possible.
Firmness
Our third-party engineers use a 170 lb mannequin in testing to simulate how weight is distributed across the surface of a mattress for the average human body. The engineers place the mannequin in the middle of the mattress and measure how far down it sinks to determine firmness. Depth of sinkage corresponds with the relative softness or firmness of the mattress. Our rating scale and associated firmness category is as follows:
- Soft: 2.9 or less
- Medium-soft: 3.0–4.4
- Medium: 4.5–5.4
- Medium-firm: 5.5–6.9
- Firm: 7.0+
Edge Support
Engineers place a 170 lb mannequin at a series of edge points along the edge of the mattress (two for foam, three for hybrids). Measurements are taken from thigh level down to a predetermined reference point, then averaged and used to calculate a total edge support score. The less the mattress sinks, the higher its edge support score. Our rating scale and associated descriptor is as follows:
- Low: 2.9 or less
- Below-average: 3.0–4.4
- Average: 4.5–5.4
- Good: 5.5–6.9
- Very good: 7.0–7.9
- Great: 8.0–8.9
- Standout: 9.0+
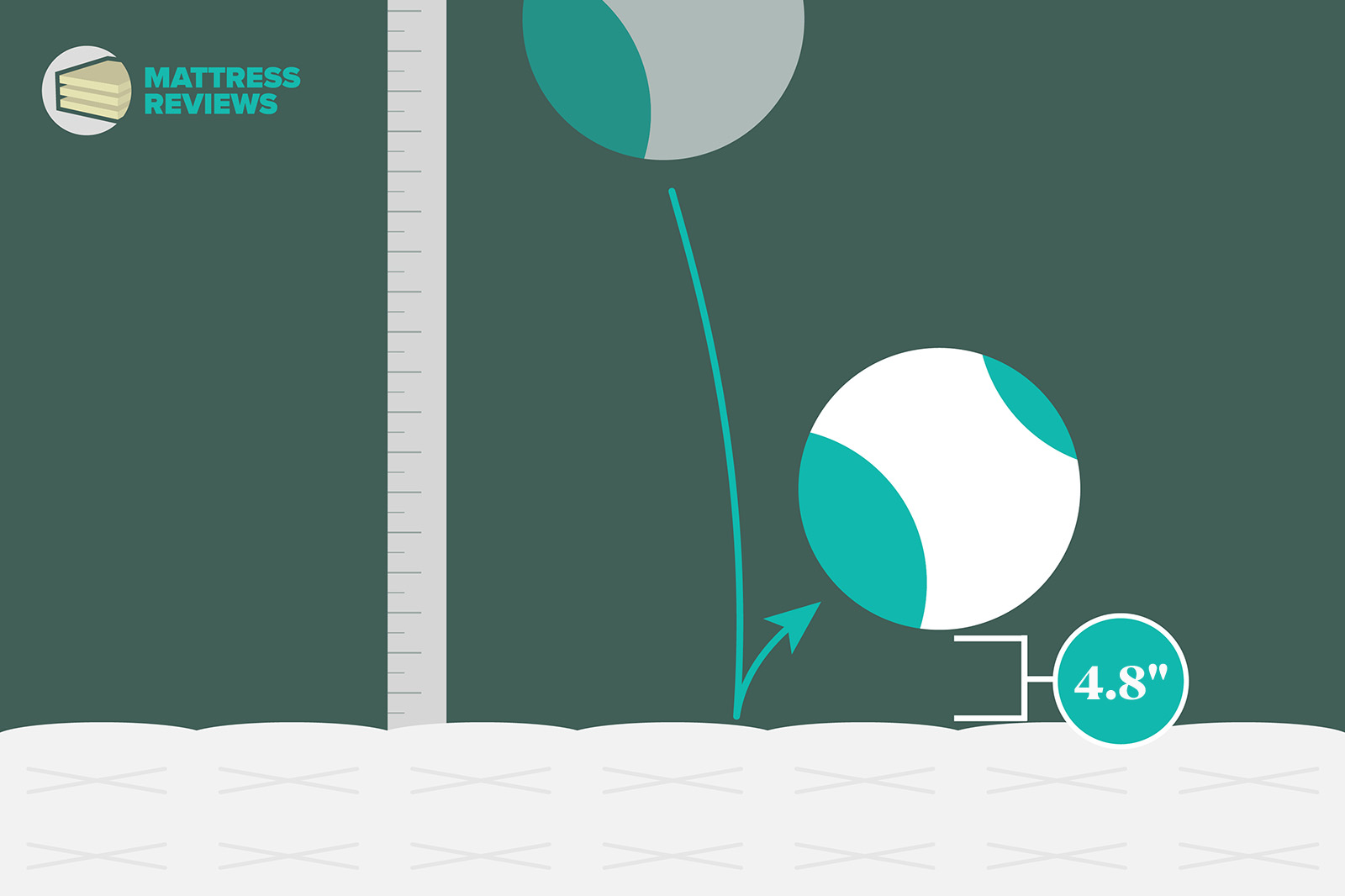
Motion Isolation
Engineers drop a medicine ball onto the mattress from a fixed position and use an accelerometer to measure the medicine ball’s impact on other parts of the mattress. High movement means less motion isolation, while low movement means high motion isolation. In situations where we do not have motion isolation testing video footage, we describe the illustrations as follows:
- Low: 2.9 or less
- Below-average: 3.0–4.4
- Average: 4.5–5.4
- Good: 5.5–6.9
- Very good: 7.0–7.9
- Great: 8.0–8.9
- Standout: 9.0+
Bounce
Engineers drop a medicine ball onto the mattress from a fixed position and measure the height of the first bounce. A higher first bounce translates to a higher bounce score on the 1–10 scale. Since some people prefer a bouncier mattress while others prefer a more consistent sleep surface, we don’t award or deduct points based on bounce score.
In situations where we do not have bounce testing video footage, we describe the illustrations as follows:
- Low: 1.0–4.4
- Mid: 4.5–6.9
- High: 7.0–10
Cooling Features
This scoring system provides a standardized assessment of cooling features in a mattress to enable informed decision-making based on temperature preferences. A mattress’s cooling score is based on the cooling features detailed by the manufacturer, with scores assigned within four weighted categories for a combined score out of 10.
Cooling feature scores are categorized as follows:
- 0–3.0: Bad
- 3.1–4.9: Mid
- 5.0–10: Good
Features are separated into “basic” and “advanced” categories. Basic cooling features are often present based on a mattress’s type (e.g., foam, hybrid); they aren’t designed to provide cooling benefits, but they naturally do by design. Advanced features, however, are additionally and intentionally included in the mattress’s construction to provide cooling benefits.

Cooling Technologies & Infusions
The mattress’s core technologies have an important role in heat regulation. Points are awarded for advanced cooling technologies such as phase-change material, gel, graphite, and copper infusions, as well as any proprietary materials that aren’t publicly detailed by the manufacturer brand. The more cooling technologies that are present in the mattress, the higher the score in this category. Weighting is 45% of the overall cooling features score.
Mattress Construction Materials
This category addresses the physical structure and materials used in mattress construction. Examples include perforated, ventilated, open-cell, and latex foams, in addition to pocketed coils and micro coils. These materials allow for improved airflow and breathability, which help keep sleep temperatures comfortable. Weighting is 35% of the overall cooling features score.
Mattress Cover Technology
This category scores the number of technologies present in a mattress’s top cover, like cooling yarn, gel-infused fabric, and moisture-wicking treatment. These technologies often feel cool to the touch, but they don’t provide the same independent cooling as the materials in the mattress itself. Weighting is 13% of the overall cooling features score.
Mattress Cover Fabric
We award points in the cover fabric category for the presence of naturally cooling materials like Tencel™ (lyocell), bamboo, wool, and Celliant. These materials keep surfaces breathable and free of moisture. However, they also affect temperature regulation less than a mattress’s internal technologies and materials. Weighting is 7% of the overall cooling features score.
Questions?
If you have questions about our testing process or suggestions for improvement, please send us an email at info@mattress-reviews.com.